CMAQ
Chemical-transport model CMAQCMAQ is a regional model - its spatial resolution ranges from a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers. The output of the model are 4D fields of pollutants for the selected area, as well as their dry and wet deposition (removal of pollutants from the atmosphere), typically with an hourly resolution.
Input data for CMAQ are 4D fields of meteorological parameters (temperature, pressure, wind, ...) and also emissions from various sources (household heating, transport, industry, system energy, agriculture) with an hourly time resolution.
The model output is calculated based on a system of integro-differential equations. These equations are calculated at each point of a regular 3D grid covering the modeled area at each step of the simulation. The physical equations in the model describe the transport and change of state of pollutants, as well as dry and wet deposition. Atmospheric chemistry equations describe the chemical transformation of pollutants, which is important in the formation of atmospheric ozone and secondary particulate matter, but also in other reactions of gaseous pollutants.
At SHMÚ we are currently working at SHMÚ with a spatial resolution of 2x2 km within the CMAQ model. Of all the models we use, CMAQ has the greatest demand on computing resources.
Examples of the outputs of the CMAQ model for Slovakia are shown in Fig. 1 - 4.
Fig. 1 and Fig. 3 show outputs for simulations run with selected emission sectors (household heating or road transport), on Fig. 2 and 4 are the outputs of the CMAQ model for a simulation with all sources and with boundary conditions that include long-distance transmission.
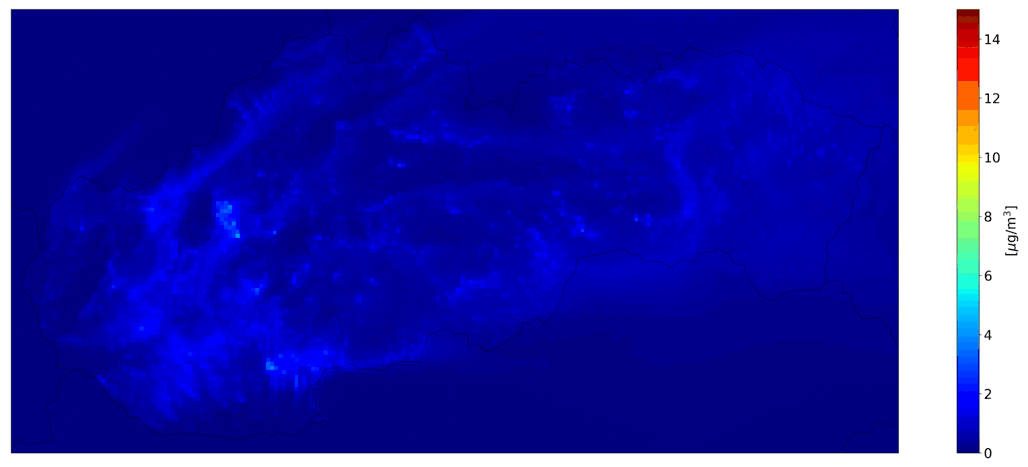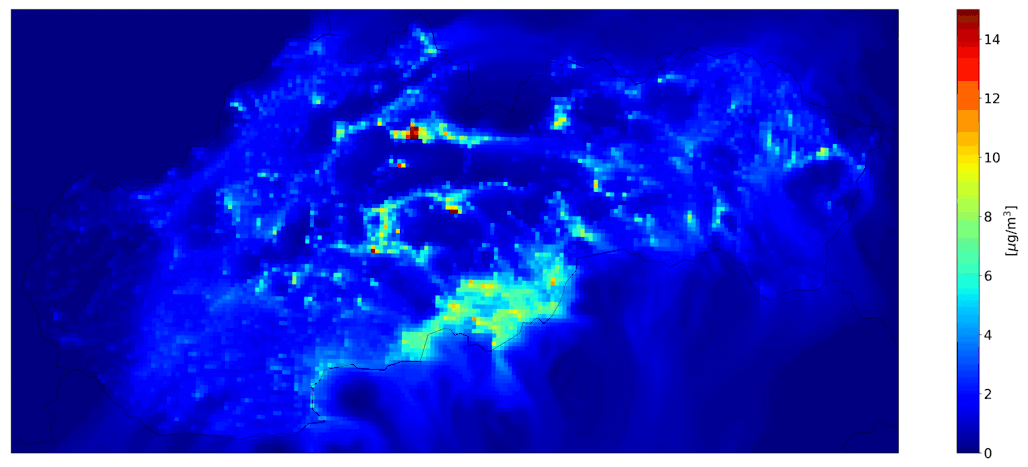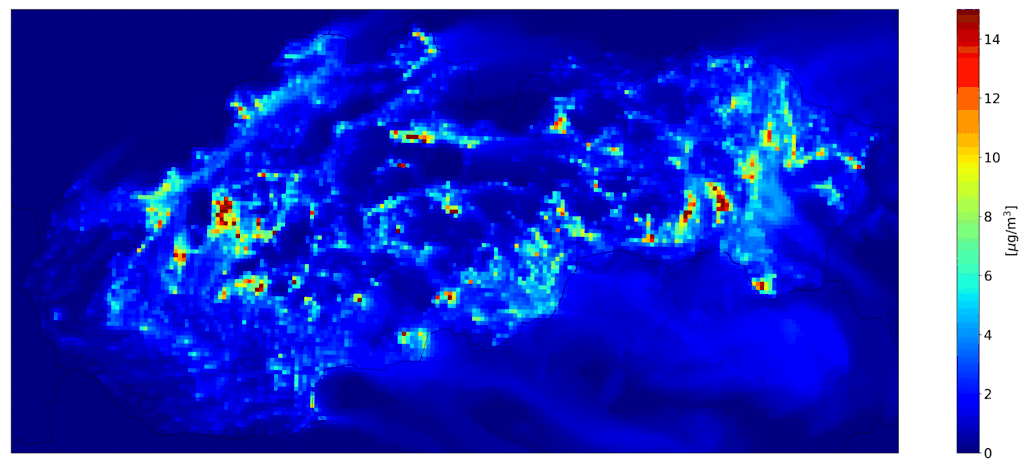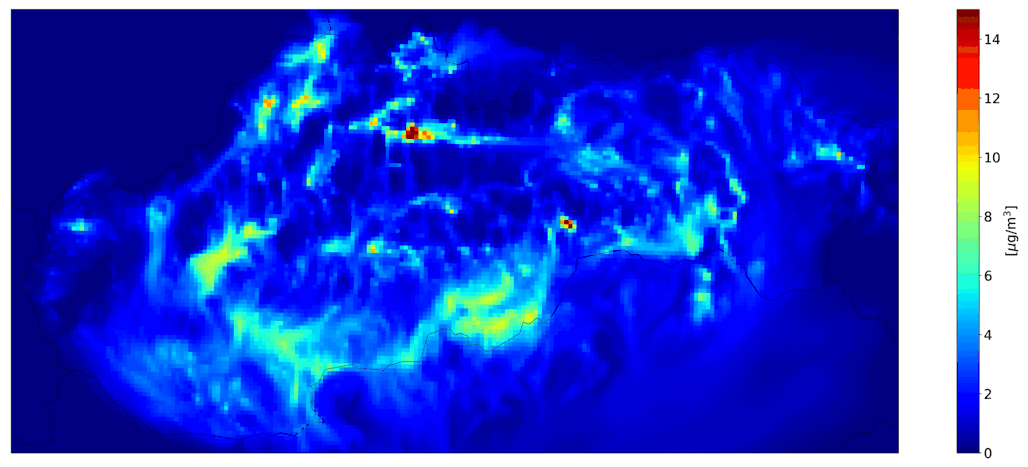
Fig. 1 Hourly mean PM10 from domestic heating, the CMAQ model output.
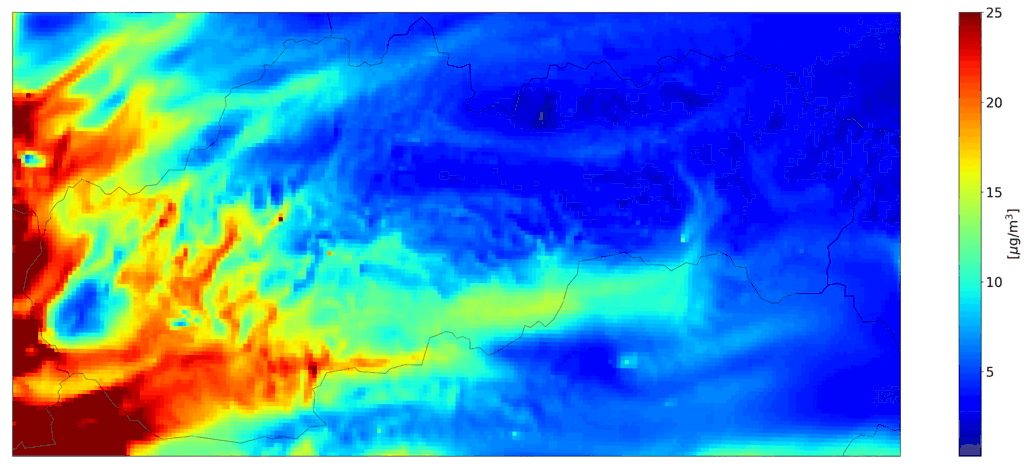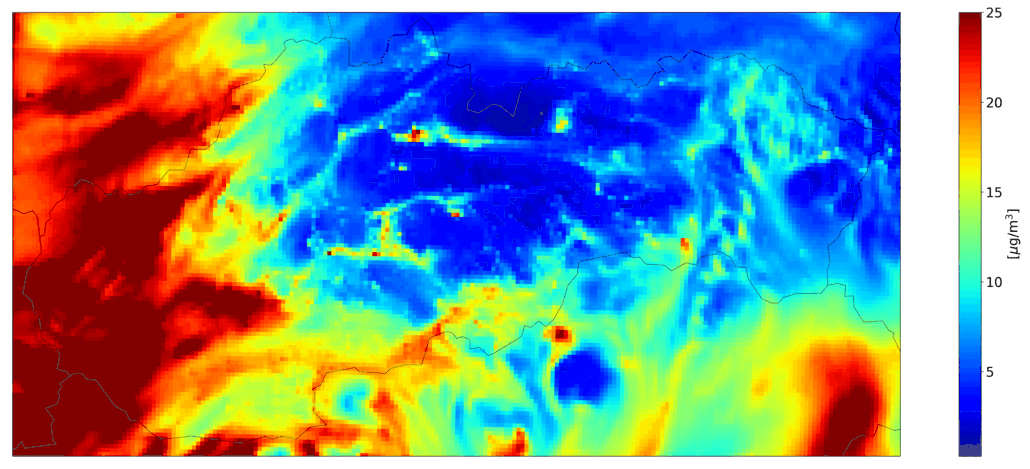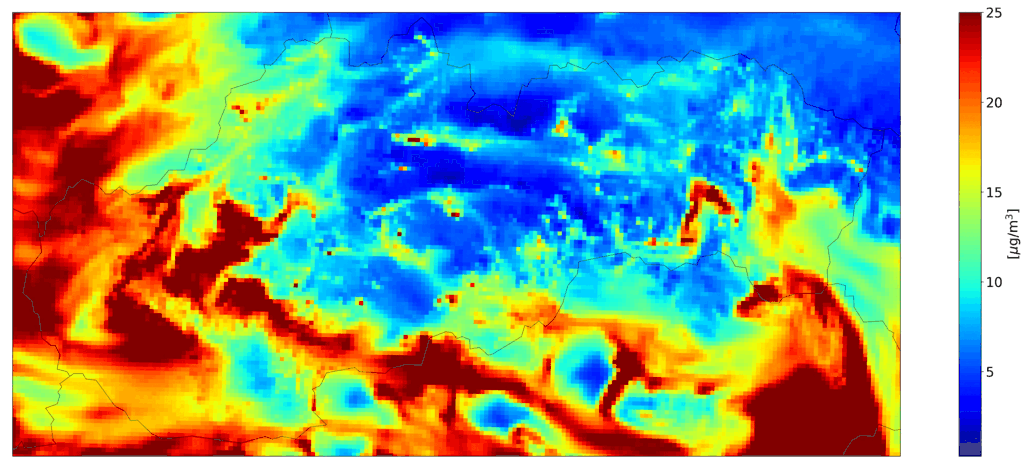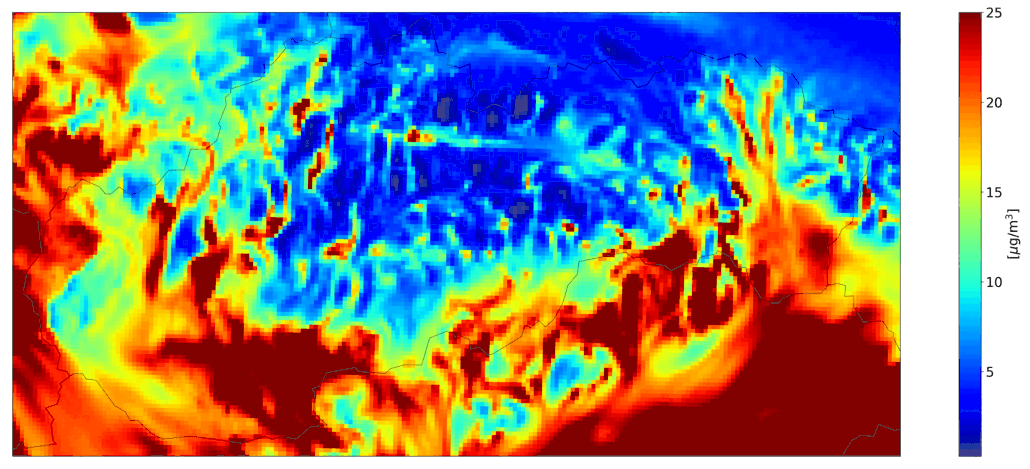
Fig. 2 Total ourly mean PM10, the CMAQ model output.
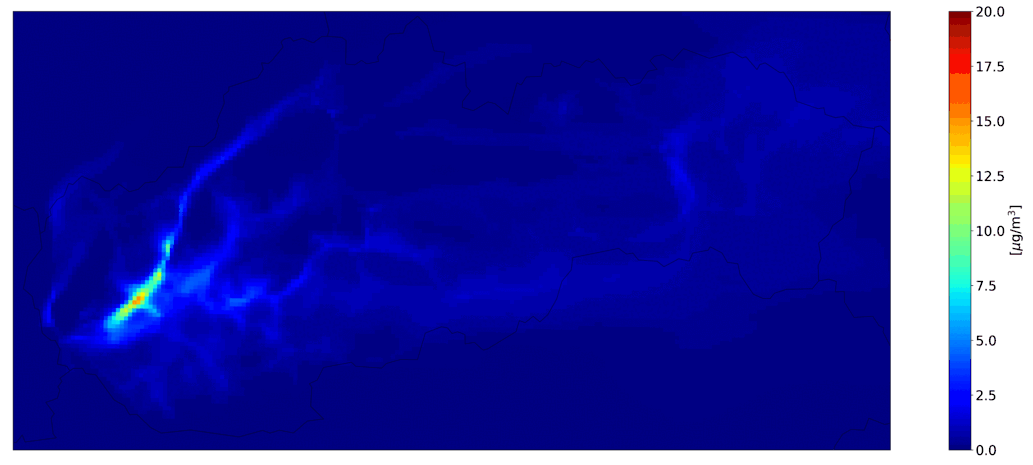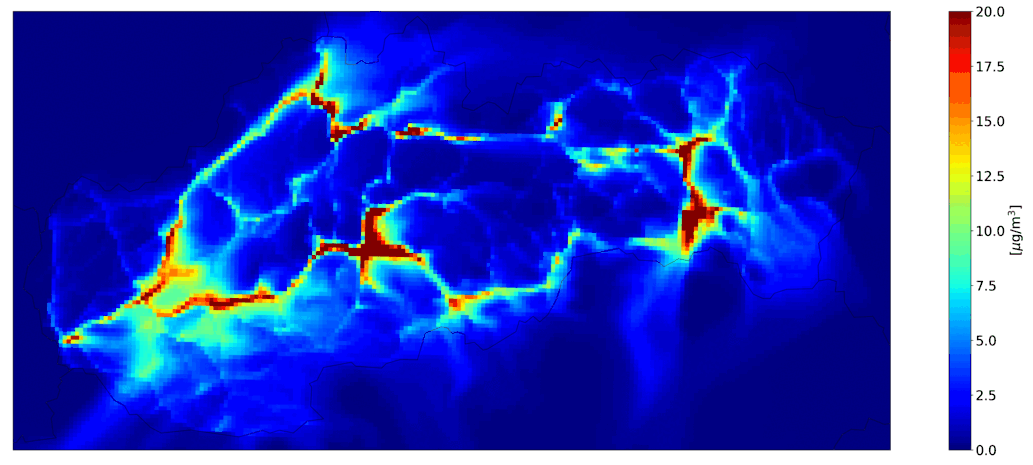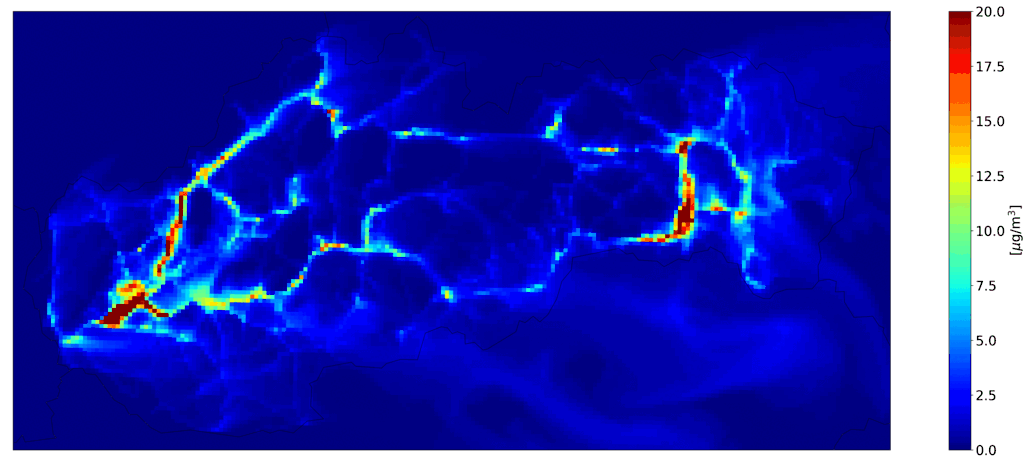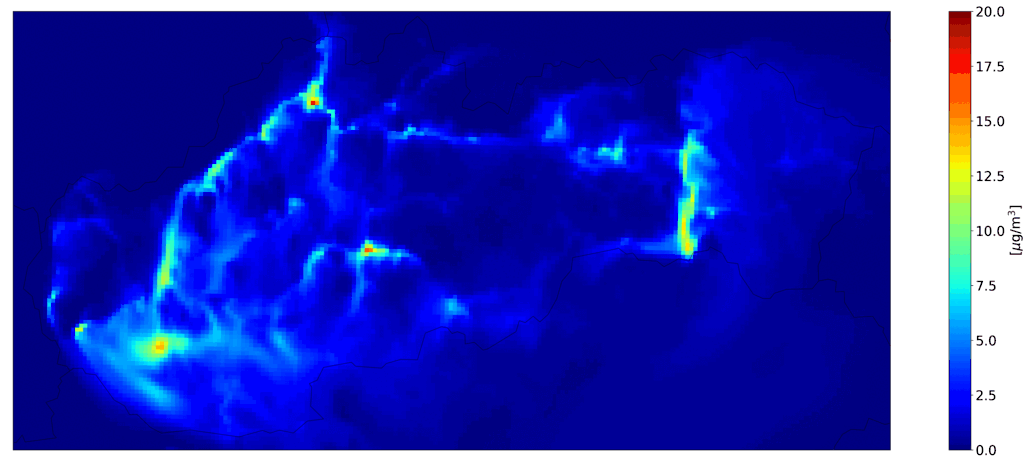
Fig. 3 Hourly mean NO2 from road transport, the CMAQ model output.
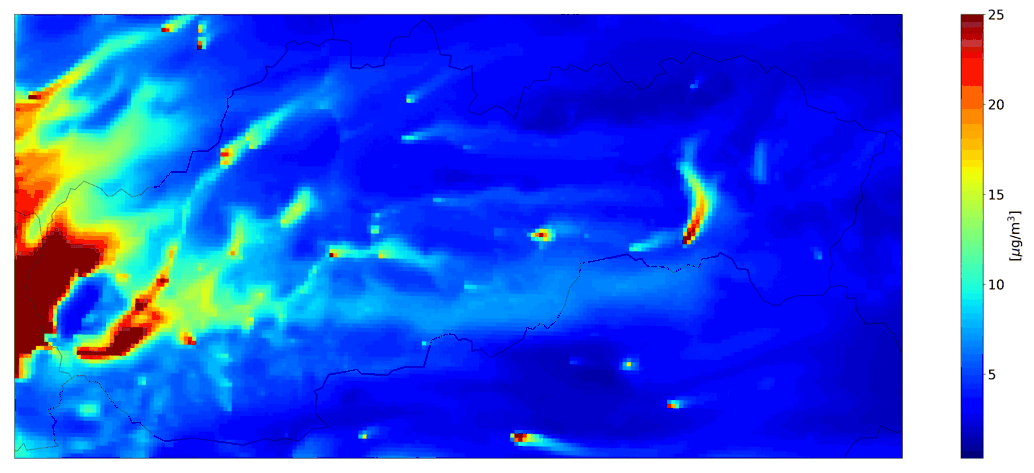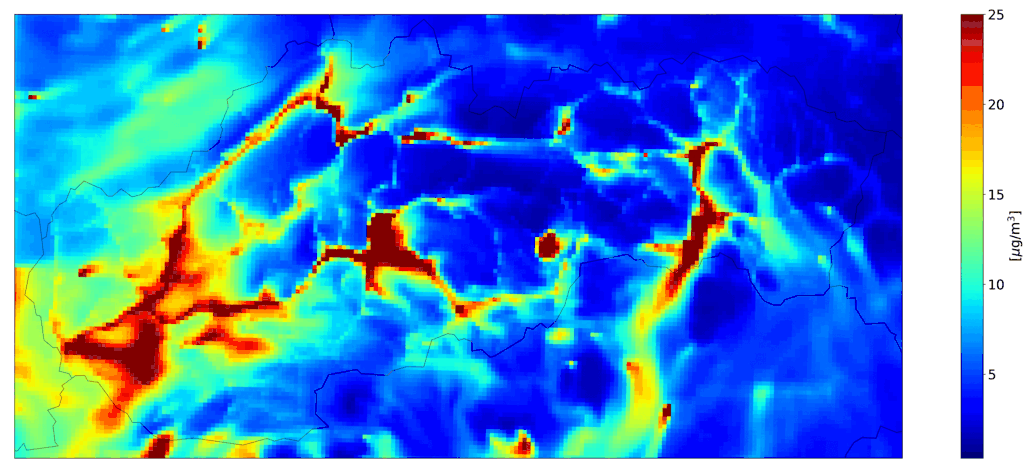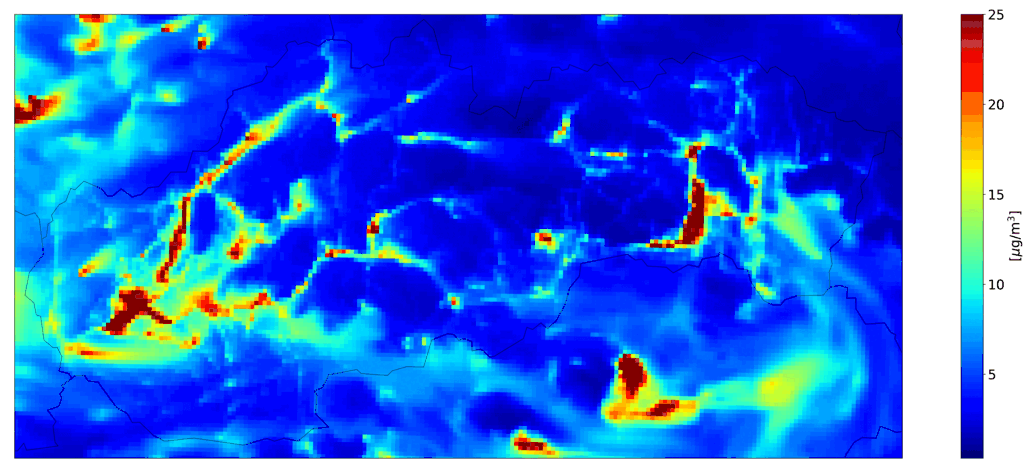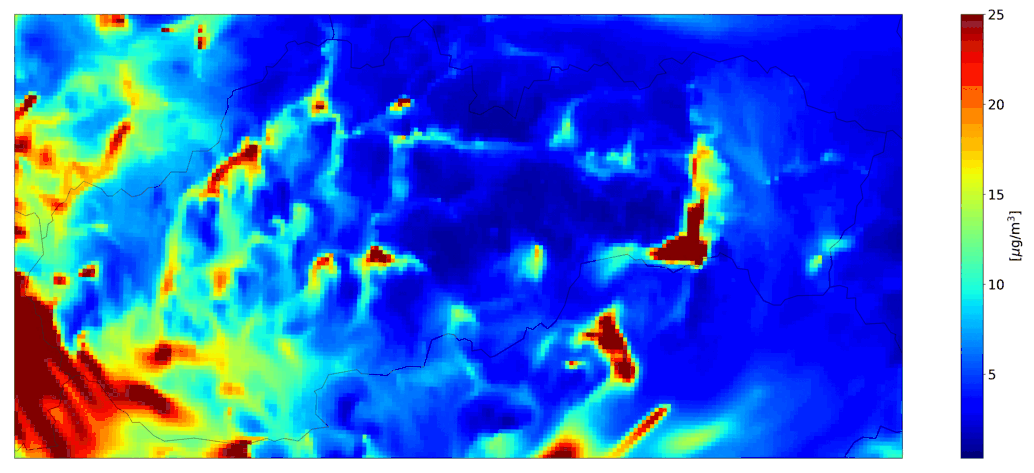
Fig. 4 Total hourly mean NO2, the CMAQ model output.
References
Byun, D W.- J.K S. Ching., 1999: SCIENCE ALGORITHMS OF THE EPA MODELS- 3 COMMUNITY MULTISCALE AIR QUALITY (CMAQ) MODELING SYSTEM. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C., EPA/600/R-99/030 (NTIS PB2000- 100561).
CMAQv5.2 Operational Guidance Document, 2017. https://www.epa.gov/cmaq/cmaq- documentation
CMAQ [Software]. Available from doi:10.5281/zenodo.107987
Selected outputs
Štefánik, D., Matejovičová, J., Krajčovičová, J., Šedivá, T., Nemček, V., Beňo, J.: Comparison of two methods of calculating NO2 and PM10 transboundary pollution by CMAQ chemical transport model and the assessment of the non-linearity effect. Atmospheric Pollution Research, Volume 11, Issue 6, 2020, p 12-23, ISSN 1309-1042, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.02.012.
Štefánik, D.: Calculation of the transboundary pollution by CMAQ chemical transport model and theassessment of the non-linearity effect 2020, 20th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, HARMO 2020.Štefánik, D., Matejovičová, J., Krajčovičová, J., , Nemček, V., Beňo, J.: Určenie koncentrácií PM10 na Slovensku v roku 2017 chemicko-transportným modelom CMAQ. Konferencia Ovzduší 2019
Štefánik, D., Matejovičová, J., Krajčovičová, J., Beňo, J., Nemček, V.: Kvalita ovzdušia v okresoch SR. Príspevok na konferencii Ochrana ovzdušia, 2019.
Šedivá, Tereza. Validation of CMAQ chemical-transport model and its meteorological inputs. Meteorologický časopis Roč. 22, č. 2 (2019), s. 77-85.Štefánik, D., Matejovičová, J., Krajčovičová, J.: Vplyv opatrení v rámci projektu LIFE-IP Malopolska na kvalitu ovzdušia na Slovensku / Príspevok na konferencii Ochrana ovzdušia, 2018.

